This is a description of the OAuth2 flow from 3rd party web sites.
In the Web Application flow (also known as the Authorization Code flow), the resource owner (a 42 user) is first redirected by the application to the OAuth authorization server at the API provider. The authorization server checks to see if the user has an active session (in our case, if the user is logged on the 42 intranet). If she does, the authorization server prompts her for access to the requested data.
After she grants access, she is redirected back to the web application and an authorization code is included in the URL as the code query parameter: http://www.example.com/oauth_callback?code=ABC1234
Because the code is passed as a query parameter, the web browser sends it along to the web server that is acting as the OAuth client. This authorization code is then exchanged for an access token using a server-to-server call from the application to the authorization server. This access token is used by the client to make API calls.
Let's see how we can implement it with the 42 API.
Redirect users to request 42 access
That's the first step. Link or redirect users to the API authorize url: https://api.intra.42.fr/oauth/authorize.
This must be properly formatted for your application and will return a permissions screen for the user to authorize. For convenience, a formatted authorize URL including your client_id is provided for each application in the apps page.
Base url
GET https://api.intra.42.fr/oauth/authorize
Parameters
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| client_id | string | Required. The client ID you received from 42 when you registered. |
| redirect_uri | string | Required. The URL in your app where users will be sent after authorization. See details below about redirect urls. |
| scope | string | A space separated list of scopes. If not provided, scope defaults to an empty list of scopes for users that don't have a valid token for the app. For users who do already have a valid token for the app, the user won't be shown the OAuth authorization page with the list of scopes. Instead, this step of the flow will automatically complete with the same scopes that were used last time the user completed the flow. |
| state | string | An unguessable random string. It is used to protect against cross-site request forgery attacks. |
| response_type | string | The response type. Ususally code. |
All this things will make together a nice and understandable URI, like:
https://api.intra.42.fr/oauth/authorize?client_id=your_very_long_client_id&redirect_uri=http%3A%2F%2Flocalhost%3A1919%2Fusers%2Fauth%2Fft%2Fcallback&response_type=code&scope=public&state=a_very_long_random_string_witchmust_be_unguessable'
Small note: when formatting the scopes parameters, be sure to read above about the distinction between application-level and token-level scopes. this has been a point of friction for some developers.
42 redirects back to your site
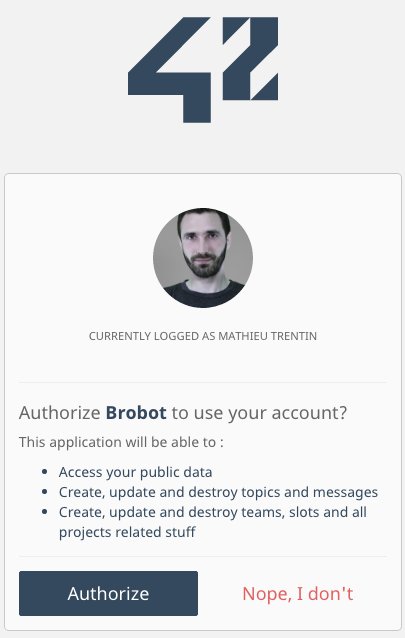 The 42 auth dialog
The 42 auth dialog
If the user grants the permission for your application to use the requested data (see scopes), it will be redirected to your redirect_uri with a temporary code in a GET code parameter as well as the state you provided in the previous step in a state parameter.
If the states don't match, the request has been created by a third party and the process should be aborted.
Exchange your code for an access token
You're almost here !
The last thing to do is a POST request to the https://api.intra.42.fr/oauth/token endpoint, with your client_id, your client_secret, the previous code and your redirect_uri. This request must be performed on server side, over a secure connexion.
Useless note: This corresponds to the token endpoint, section 3.2 of the OAuth 2 RFC. Happy ?
Base url
POST https://api.intra.42.fr/oauth/token
Parameters
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| grant_type | string | Required. The grant type. In this case, it's authorization_code. |
| client_id | string | Required. The client ID you received from 42 when you registered. |
| client_secret | string | Required. The client secret you received from 42 when you registered. |
| code | string | Required. The code you received as a response to Step 1. |
| redirect_uri | string | The URL in your app where users will be sent after authorization. |
| state | string | The unguessable random string you optionally provided in Step 1. |
For example, with curl:
curl -F grant_type=authorization_code \
-F client_id=9b36d8c0db59eff5038aea7a417d73e69aea75b41aac771816d2ef1b3109cc2f \
-F client_secret=d6ea27703957b69939b8104ed4524595e210cd2e79af587744a7eb6e58f5b3d2 \
-F code=fd0847dbb559752d932dd3c1ac34ff98d27b11fe2fea5a864f44740cd7919ad0 \
-F redirect_uri=https://myawesomeweb.site/callback \
-X POST https://api.intra.42.fr/oauth/token
Make API requests with your token
Include your token in all your requests in a authorization header:
Authorization: Bearer YOUR_ACCESS_TOKEN
For example, you can fetch the current token owner, with curl:
curl -H "Authorization: Bearer YOUR_ACCESS_TOKEN" https://api.intra.42.fr/v2/me
# {"id":23,"email":"30_1@staff.42.fr","login":"30_1","url":"http://localhost:13000/v2/users/30_1","phone":"0611041698","displayname":"Mathieu Trentin","image_url":"https://cdn.intra.42.fr/userprofil/30_1.jpg","staff?":true,"correction_point":5,"pool_month":null,"pool_year":null,"location":null,"wallet":5,"groups":[{"id":3,"name":"pixel"},{"id":1,"name":"staff"}],"cursus":[{"cursus":{"id":1,"name":"42","created_at":"2014-11-02T16:43:38.480Z","updated_at":"2016-05-25T14:33:59.420Z","slug":"42","kind":"normal"},"end_at":null,"level":0.0,"grade":"Midshipman","projects":[],"skills":[]},{"cursus":{"id":4,"name":"Piscine C","created_at":"2015-05-01T17:46:08.433Z","updated_at":"2016-06-07T17:09:43.612Z","slug":"piscine-c","kind":"normal"},"end_at":null,"level":0.0,"grade":null,"projects":[],"skills":[]}],"achievements":[...],"titles":[],"partnerships":[],"patroned":[],"patroning":[],"expertises_users":[],"campus":[{"id":1,"name":"Paris","time_zone":"Paris","language":{"id":1,"name":"Français","identifier":"fr","created_at":"2014-11-02T16:43:38.466Z","updated_at":"2016-06-08T13:40:28.805Z"},"users_count":5929,"vogsphere_id":1}]}
If you can't modify http headers, you can send your token as a
access_tokenparameter.